Data store description form
Data Store Object
Overview
Data stores connect Appian to external relational databases in order to store and retrieve application data. This page covers how to create data stores, run DDL scripts, and retrieve external data in your application.
Data stores allow you to insert, update, query, and delete data in the format needed by your applications without writing structured queries (SQL). You must have a business data source configured to use this feature.
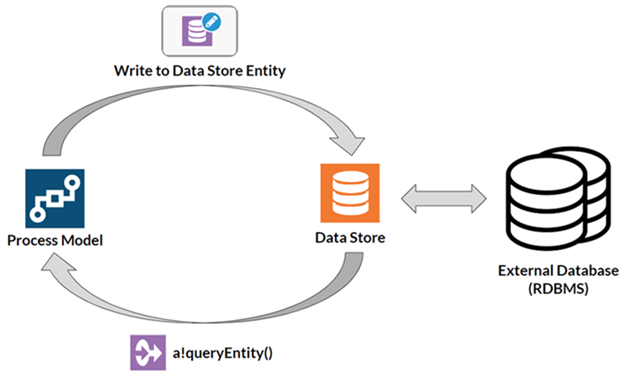
Custom data types are used by your processes to store data in an external relational database. The relationships between these custom data types are used to create tables and keys in the database that are associated with through the data store.
Once you define a custom data type and map it to a data store entity, you can update data in the database using the Write to Data Store Entity Smart Service. You can also use a!queryEntity() to retrieve information through the data store, without knowing the underlying table schemas of the database or SQL.
Create
To create a data store, complete the following:
- In the Build view, click NEW > Data Store.
- Configure the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|
| Name | Enter a name that follows the recommended naming standard. |
| Description | Enter a brief description. |
| Data Source | Select a source from the available list. The sources in the list correspond to any relational databases configured for your environment. |
Once you've created the data store, you need to map your custom data types to the external database by adding entities to the data store.
To add an entity to the data store:
- Click Add Entity. An entity dialog displays.
- In the first box of the dialog, enter a name for the new entity.
- In the second box of the dialog, browse to and select a custom data type from the list of available CDTs.
- Click Save.
Once you've added at least one entity, you can publish the data store.
To publish the data store:
- Click Verify to validate that the necessary data structures have been created in the database, and that the database is available.
- When the tables needed for your entity do not already exist (expected) the following message is displayed: No matching tables found!
- If the letter casing for the schema in Oracle is different than the schema attribute of the @Table annotation of the XSD (which is lowercase by default), the entity will not be able to map to the table. If you encounter this issue, you can create a synonym in the Appian user schema that points to the tables in the other schema. Please note that the synonym will need to have the same name as the table or view that it points to.
- Select Create tables automatically to have the system execute the SQL commands needed to configure your data store entity - OR - select Create tables manually if you want or need to have the necessary SQL commands executed using a process that you perform outside the system.
See below: Running DDL Scripts
- If you selected Create tables automatically and want Appian to always execute DDL statements, check the Automatically Update Database Schema checkbox on the data store's page. If automatic schema updates are enabled both globally in the Admin Console and locally on the data store, Appian automatically attempts to fix any discrepancies between your database schema and data store definition by adding, but never removing or altering, tables and columns to the database to match entity definitions.
- When automatic schema updates are enabled:
- Columns and tables missing from the database, but present in the data type, are created.
- Columns and tables missing from the data type, but present in the database, remain untouched.
- Columns that are incorrectly configured to map to a data type field are not altered, so verification of the data store requires manual changes to the database. An example that requires manual changes is altering a database column of type text so that it maps to a data type field of type integer. Additionally, fields renamed from the Data Type Designer are considered entirely new, not renamed, and a column is added if not present on the database.
- If automatic schema updates are disabled, Appian does not address any discrepancies between your database schema and data store definition. This means:
- Tables missing from the database are not automatically created.
- Columns missing from tables are not added.
- When automatic schema updates are enabled, new columns and tables are automatically added to the data store's schema in the following scenarios:
- The data store is imported into an environment for the first time.
- Changes to the data store are imported.
- A designer updates a data type used by the data store (precedent data type).
- WARNING: Existing column definitions are not updated. For example, Appian will not make changes to a column's type or length.
- For automatic schema updates to be considered "enabled," it must be enabled both globally in the Admin Console and locally on the data store
- If the database is not available or you want to avoid updating the database immediately, click Save Draft.
- Click Save and Publish.
Running DDL Scripts
When creating or editing a data store entity, the system checks your RDBMS to see if the necessary data structures already exist.
When the data structures in your database do not match, you are given the option to create tables manually with a link to download the SQL needed to generate the necessary structure.
To create tables manually, complete the following:
- After selecting Create tables manually, click Download DDL Script.
- The browser's File Download dialog displays, listing the DDL script file for download.
- The script file is named using the following convention: DDL.sql
- Optionally, you can edit the file name to use your own version numbering scheme for your DDL scripts, such as: DDL__.sql .
- Save the file to your local machine.
- Review the script or have it reviewed by your database administrator (DBA) to ensure that it meets your organization's requirements.
- If the script does not meet your requirements, you can modify your custom data type to better suit your needs by completing the following:
- Edit the custom data type that was used by the entity that you were creating or updating.
- Edit the Data Store entity to use the new custom data type. You can skip this step if you updated all outdated dependents when editing the data type.
- Verify the Data Store again to generate a new DDL script.
- If the script meets your organization's requirements, run the DDL script to create the necessary tables for your data store entity.
- Click Verify Again.
- When the database tables are properly defined, the message Entity mappings verified displays.
- If the database tables are not properly defined, use the commented commands in the DDL script to drop and recreate the tables.
Edit
All data store attributes can be edited by users with Editor or Administrator permissions. The following list details how to edit each attribute:
- Click on the name or description to edit them in place.
- Update the data source by selecting one from the list of available data sources.
- Check the Automatically update database schema checkbox to allow Appian to execute DDL SQL statements when dependent data types are updated or when this data store is imported. Changes to this attribute do not take effect in the environment if the auto-update feature has been disabled from the Admin Console.
- Click an entity to modify its name or its data type.
- Click Add Entity to configure a new data store entity.
After making any of the above edits, you may either save a draft or publish a new version of the data store. To save a draft, click Save Draft. Saving a draft does not affect the environment or execute SQL DDL statements, but you may come back to the data store at any time to view and publish the changes. To publish a new version of the data store, follow these steps:
- Click Verify to validate your data store edits.
- When the tables needed for your entity must be modified (expected) the following message is displayed: No matching tables found!
- Select Create tables automatically to have the system execute the SQL commands needed to configure your data store entity - OR - Select Create tables manually if you want or need to have the necessary SQL commands executed using a process that you perform outside the system. See Running DDL Scripts for additional details.
- Click Save & Publish.
Delete
Note: Take care when deleting a data store not to disrupt any active processes that query or write to the data store.
- Go to an application that contains the data store.
- Select it in the grid and then click the Delete button in the grid toolbar.
System administrators have the ability to delete data stores (and other objects) in bulk by selecting them and clicking Delete in the toolbar.
Security
Tip: A user must have at least Viewer permissions to a data store in order to use its entities to query, write, or delete data.
The security role map of a data store controls which users can see or modify it and its properties. By default, only the data store creator and system administrators have access to the data store. See Editing Object Security to modify a data store's security.
The following table outlines the actions that can be completed for each permission level in a data store's security role map:
| Actions | Administrator | Editor | Viewer | Deny |
|---|
| Retrieve entity to read/write at runtime* | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| View the data store definition | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Update the data store definition | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| View the security | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Update the security | Yes | No | No | No |
| Save & Publish the data store | Yes | No | No | No |
| Delete the data store | Yes | No | No | No |
*Users must have at least Viewer permissions to the data store in order to read or write data using the Write to Data Store smart service.
Retrieving External Data
Use the following guidelines when loading data into a data store from an external RDBMS.
Perform Bulk Operations as Much as Possible
Minimize the number of individual queries to the database.
You can write arrays of data to your data store using the Write to Data Store Entity Smart Service, so there is no need to run multiple instances to write data to a single entity. To write multiple data types, you can use the Write to Multiple Data Store Entities Smart Service.
Retrieve Data in Smaller Batches
The amount of data that can be returned by a query is limited to 1MB by default. If you expect to return more than 1MB of data, you can design your process models to retrieve data in smaller batches and loop the process flow to retrieve the desired data.
When using a query to start processes, you may quickly reach the default limit of 1000 activated instances by repeatedly activating your Send Message Event and gateways (which do not provide the option to delete previously completed instances in the same manner as process flow activities).
You may want to configure your Send Message Event in a subprocess and configure the node properties to delete the completed instances when they are no longer needed.
You can also configure the other process activities to automatically delete previously completed instances to avoid reaching the 1000 node limit. This setting also reduces memory (RAM and HD) usage of your processes.
See Also
- Configuring Relational Databases
- Database Schema Best Practices


